Top 10 Safety Valve Types for Optimal Pressure Control and System Safety
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial safety, the critical role of safety valves cannot be overstated. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in pressure management systems, "The reliability of a safety valve can mean the difference between seamless operation and catastrophic failure." As industries grow and technology advances, understanding the various types of safety valves available becomes essential for optimal pressure control and overall system safety.
Safety valves serve as a vital component in preventing overpressure conditions, ensuring the integrity of equipment and the safety of personnel. With numerous designs and applications, selecting the appropriate safety valve type can significantly impact an organization's ability to maintain efficient operations while safeguarding against potential hazards. From spring-loaded designs to pilot-operated variants, the diversity in safety valve types highlights the necessity for thorough knowledge and expertise in this area.
As we delve into the top 10 safety valve types for optimal pressure control, it is imperative to explore their unique features, advantages, and best practices for implementation. By equipping ourselves with this knowledge, we can contribute to a safer industrial environment and enhance the overall reliability of pressure management systems across various sectors.

Top 10 Types of Safety Valves Used in Industrial Applications
Safety valves play a critical role in maintaining pressure control and ensuring system safety in various industrial applications. Among the top types of safety valves used, the spring-loaded safety valve is the most prevalent due to its simplicity and reliability. According to a report by the International Society of Automation, approximately 70% of safety valves installed in process industries are of the spring-loaded type. These valves automatically relieve excess pressure, preventing possible catastrophic failures in systems that handle volatile or hazardous substances.
Another widely used safety valve type is the pilot-operated safety valve. These valves are particularly effective in high-pressure settings and are gaining popularity in industries such as petrochemical and natural gas. A study published in the Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology indicates that pilot-operated valves can provide a more stable response under fluctuating pressure conditions compared to their spring-loaded counterparts. Additionally, they're designed to minimize the loss of product during operation, making them a cost-effective choice for manufacturers focused on efficiency.
In applications involving steam or corrosive fluids, balanced bellows safety valves are often employed. These valves are engineered to handle back pressure effectively, ensuring reliable performance in challenging environments. Recent market research anticipates a growth rate of 5.6% in the demand for specialized safety valves over the next five years, driven by increased safety regulations and the need for improved system reliability across industries.
Top 10 Safety Valve Types for Optimal Pressure Control and System Safety
| Safety Valve Type | Description | Application | Pressure Range (PSI) | Temperature Range (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring Loaded Safety Valve | A valve that opens when the pressure exceeds a set limit due to a spring mechanism. | Steam and gas applications. | 30 to 450 PSI | -20 to 500 °F |
| Pilot Operated Safety Valve | Uses a pilot signal to control the main valve opening, offering higher accuracy. | Pressure systems with varying pressure levels. | 100 to 3000 PSI | -40 to 650 °F |
| Balanced Safety Valve | Designed to minimize the effect of back pressure on the valve. | Liquid and gas applications with high backpressure. | 15 to 600 PSI | -10 to 450 °F |
| Dead Weight Safety Valve | Relies on the weight of a piston to maintain pressure balance. | Used in high-pressure steam systems. | 200 to 4000 PSI | -20 to 550 °F |
| Thermal Relief Valve | Automatically opens to relieve pressure caused by thermal expansion. | Hydraulic systems and storage tanks. | 10 to 250 PSI | -40 to 300 °F |
| Safety Relief Valve | Combines features of safety valves and relief valves, suitable for liquid and gas. | Oil and gas operations. | 50 to 1500 PSI | -40 to 400 °F |
| Piston Safety Valve | Uses a piston mechanism to open and close, suitable for high-pressure environments. | Chemical processing industries. | 500 to 6000 PSI | -20 to 750 °F |
| Vacuum Relief Valve | Prevents vacuum conditions that can collapse tanks. | Storage tanks and pipelines. | Not applicable | -40 to 150 °F |
| Check Valve and Relief Combo | Combines check and relief capabilities in one valve. | Various fluid systems requiring backflow prevention. | 20 to 700 PSI | -20 to 300 °F |
Importance of Safety Valves in Pressure Control and System Integrity
Safety valves play a crucial role in maintaining pressure control and ensuring the integrity of various systems. They serve as vital components designed to automatically release excess pressure that can build up within a vessel or pipeline. This is essential in preventing potential failures, which could lead to catastrophic incidents such as explosions or leaks. By functioning as a fail-safe mechanism, safety valves help uphold safe operating conditions, protecting both equipment and personnel in environments where pressure fluctuations are inevitable.
In industries ranging from oil and gas to chemical processing, the integrity of operations heavily relies on effective pressure management. The significance of safety valves extends beyond mere compliance; they embody a proactive approach to system safety. By understanding the types of safety valves available and their specific applications, industry professionals can select the most suitable option for their operational needs. This choice directly influences not only the reliability of the system but also maximizes efficiency and minimizes downtime, thereby contributing to the overall safety and productivity of industrial processes.
Top 10 Safety Valve Types for Optimal Pressure Control
Comparison of Common Safety Valve Materials and Their Performance
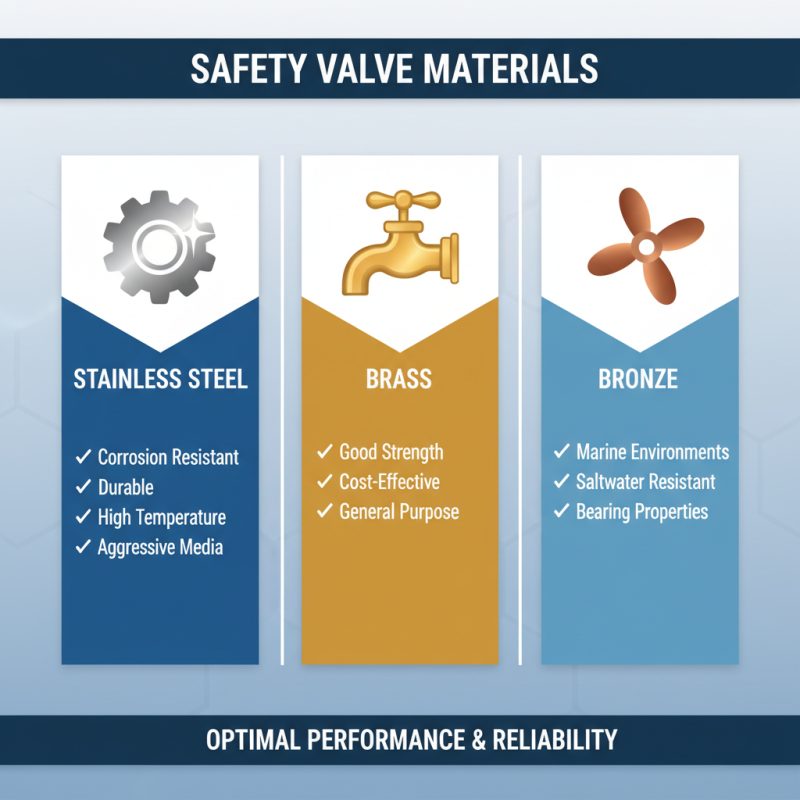
When selecting a safety valve, the material used in its construction plays a crucial role in determining performance and reliability. Common materials for safety valves include stainless steel, brass, and bronze, each with distinct characteristics. Stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance and durability, making it an ideal choice in environments with aggressive media or high-temperature operations. Its strength ensures long-term stability, reducing the chances of failure during critical applications.
Brass and bronze, on the other hand, are widely used in applications where lower temperatures and pressures prevail. These materials provide excellent machinability and resistance to wear, though they may not perform as well under extreme conditions compared to their stainless steel counterparts. Additionally, they are often more cost-effective, making them a popular choice for many industrial applications. Selecting the right material depends on various factors, including operating conditions, media compatibility, and economic considerations, ultimately impacting the overall safety and efficiency of the system.
Industry Standards and Regulations Governing Safety Valve Design

Safety valves play a crucial role in maintaining pressure within systems across various industries, ensuring operational safety and equipment integrity. The design of these valves is governed by a range of industry standards and regulations, which dictate their performance characteristics, materials, and testing procedures. Organizations such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provide guidelines that define the minimum requirements for the manufacture and testing of safety valves. Compliance with these standards helps to ensure that safety valves operate effectively in protecting systems against overpressure conditions.
The regulatory framework surrounding safety valve design also includes considerations for environmental impact and operational reliability. For instance, safety valves must be designed to minimize leakages and optimize performance under different environmental conditions. In many jurisdictions, national and international regulations require regular inspection and maintenance of safety valves to ensure ongoing compliance and functionality. This ongoing oversight emphasizes the significance of adhering to established standards, as it safeguards the safety of personnel, equipment, and the surrounding environment in high-pressure systems.
Recent Trends in Safety Valve Technology and Innovations
Recent advancements in safety valve technology have significantly influenced optimal pressure control and system safety in industrial applications. Recent trends indicate a shift towards smart safety valves that integrate IoT capabilities, enabling remote monitoring and diagnostics. A report by MarketsandMarkets forecasts that the global smart valve market will reach USD 2.5 billion by 2025, driven by the need for enhanced safety measures and real-time data analysis. These innovations not only improve efficiency but also reduce the risk of accidents caused by system failures.
One of the most notable trends is the development of advanced materials and designs that enhance the reliability and performance of safety valves. For instance, new polymers and alloys are being utilized to withstand corrosive environments and high temperatures, which prolongs the lifespan of these critical components. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), the use of advanced materials can increase valve lifespan by up to 30%, thereby decreasing maintenance costs and downtime.
Tips: When selecting a safety valve, it’s crucial to consider both the application requirements and the latest technology trends. Opting for valves with smart monitoring features can provide real-time insights, allowing for proactive maintenance and improved safety compliance. Additionally, staying informed about advancements in materials can help in choosing a valve that meets operational demands while ensuring longevity and reliability.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Importance of Safety Relief Valves in Industrial Applications: A Comprehensive Guide
-

Understanding the Importance of Safety Valves in Industrial Applications
-

2025 Top 5 Safety Relief Valve Innovations You Should Know
-

Understanding the Importance of Relief Valves in Industrial Applications
-

Maximizing System Efficiency: The Critical Role of Relief Valves in Preventing Pressure Surges
-

2025 How to Choose the Right Pressure Safety Valve for Optimal System Efficiency
